pc building opens up a world of possibilities for tech enthusiasts and casual users alike, inviting you to create a personalized computer that fits your unique needs. From selecting the right CPU and GPU to ensuring optimal cooling, each step in the building process is a rewarding journey filled with learning and innovation.
This guide delves into the essential components necessary for a successful build, walking you through each part’s function and performance impact. We’ll also provide a clear, step-by-step assembly process, along with tips for troubleshooting common issues, ensuring that both beginners and experienced builders can navigate the process with confidence.
Essential Components for PC Building

Building a personal computer requires a careful selection of essential components that work together to deliver optimal performance. Each component plays a specific role in the overall functionality, ensuring that the system runs smoothly and efficiently. This guide will delve into the key components needed for a successful PC build, providing insights into their functions and the various options available in the market.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU is often referred to as the brain of the computer. It processes instructions and performs calculations that drive applications and games. When choosing a CPU, consider factors such as clock speed, core count, and thermal design power (TDP). Popular brands include Intel and AMD, with Intel’s Core i9 series and AMD’s Ryzen 9 series being high-performance options.
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
The GPU is crucial for rendering images and video, especially in gaming and graphic design. A powerful GPU enhances the visual experience and ensures smooth frame rates. NVIDIA and AMD are the two leading manufacturers, with NVIDIA’s RTX 30 series and AMD’s RX 6000 series being prominent choices for high-end gaming.
Motherboard
The motherboard acts as the backbone of the PC, connecting all components and facilitating communication between them. It houses the CPU, RAM, and provides slots for GPU and storage. When selecting a motherboard, consider the chipset, form factor, and expansion options. Brands like ASUS, MSI, and Gigabyte offer a range of motherboards with various features.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM is essential for multitasking and overall system speed, as it temporarily stores data for applications in use. Modern systems generally require at least 16GB of RAM for optimal performance. Key brands include Corsair, G.Skill, and Kingston, with options ranging from DDR4 to DDR5 memory, which can significantly impact performance depending on the use case.
Storage
Storage options can greatly affect boot times and load speeds. There are two primary types: SSDs (Solid State Drives) and HDDs (Hard Disk Drives). SSDs are faster and more reliable, while HDDs offer more storage capacity for less cost. Brands like Samsung and Western Digital provide a variety of storage solutions, including NVMe SSDs for superior performance.
Power Supply (PSU)
The power supply converts electrical power from the outlet into usable power for the computer components. A reliable PSU is vital for system stability and longevity. Factors to consider include wattage, efficiency rating (80 PLUS certification), and modularity. Brands like EVGA, Corsair, and Seasonic offer high-quality power supplies that cater to various needs.
Each component’s compatibility and performance can significantly influence your overall PC experience, making informed choices essential when building a custom system.
Comparison of Brands and Models
It’s important to compare different brands and models to find the best components that fit your needs and budget. Below is a table summarizing notable characteristics of selected brands for each component:
| Component | Brand/Model | Key Features | Price Range (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i9 | High clock speed, multi-core performance | $500-$600 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 | Excellent multi-threading, competitive pricing | $400-$500 | |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX 3080 | Ray tracing, AI-enhanced gaming | $700-$900 |
| AMD RX 6800 XT | Strong 4K gaming performance | $600-$800 | |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix | Gaming-oriented features, robust power delivery | $200-$300 |
| MSI MAG B550 | Good value, decent features for Ryzen | $150-$250 | |
| RAM | Corsair Vengeance LPX | High speed, reliable performance | $80-$150 |
| G.Skill Ripjaws V | Great overclocking capabilities | $70-$140 | |
| Storage | Samsung 970 EVO NVMe SSD | Fast read/write speeds, reliable | $100-$200 |
| Western Digital Blue HDD | High capacity, cost-effective | $50-$100 | |
| Power Supply | EVGA SuperNOVA | High efficiency, fully modular | $100-$200 |
| Corsair RMx Series | Whisper-quiet operation, solid performance | $90-$180 |
Step-by-Step PC Building Process
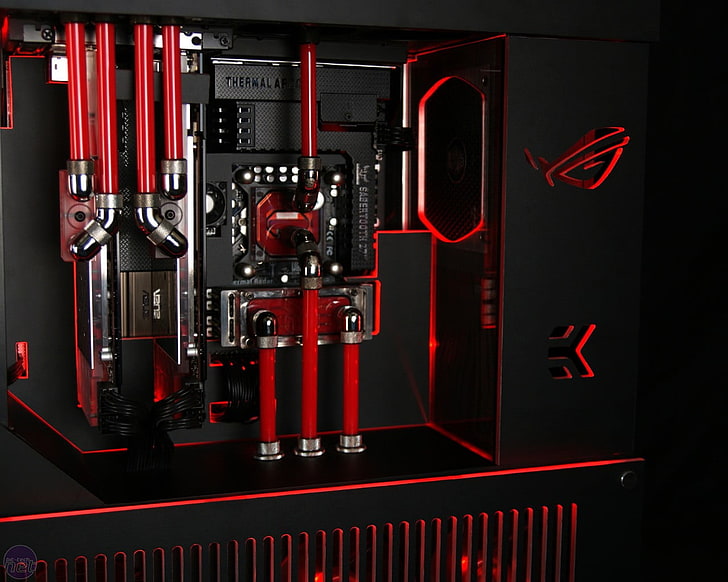
Building a PC can seem daunting, but with a structured approach and a clear understanding of each step, it becomes an exciting project. This guide walks you through the entire process of assembling your computer, from gathering your components to powering it on for the first time.
Before diving into the assembly, it’s essential to gather all necessary tools and equipment. Having the right tools on hand ensures that the building process runs smoothly and minimizes the risk of damaging any components.
Required Tools and Equipment
To successfully build a PC, you’ll need a few basic tools and equipment. Having these items ready will facilitate a more organized and efficient assembly process:
- Phillips Head Screwdriver: A medium-sized Phillips head screwdriver is essential for securing components and fastening screws.
- Anti-Static Wrist Strap: This will help prevent static electricity from damaging sensitive components during assembly.
- Thermal Paste: This may be needed if your CPU cooler does not come with pre-applied thermal paste.
- Cable Ties: Useful for organizing and securing cables for better airflow and aesthetics.
- Flashlight: A small flashlight can help illuminate dark corners inside the case for easier installation.
Assembling the PC Step-by-Step, Pc building
The assembly process involves several distinct steps to ensure a successful build. Follow these steps carefully for best results:
- Prepare the Case: Begin by removing the side panels of your case to access the interior. Ensure that the workspace is clean and free of clutter.
- Install the Power Supply: Secure the power supply unit (PSU) into its placed mounting area, ensuring the fan is positioned correctly for optimal airflow.
- Install the Motherboard: Align the motherboard with the standoffs in the case and secure it using the screws provided. Double-check that it sits flat and all ports are accessible.
- Insert the CPU: Open the CPU socket lever, align the CPU with the socket, and gently place it in. Close the lever to secure it in place.
- Apply Thermal Paste and Install the CPU Cooler: If thermal paste is not pre-applied, add a small pea-sized amount to the center of the CPU and attach the cooler. Secure it in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Install RAM Modules: Locate the RAM slots and insert the RAM sticks into their respective slots until you hear a click, indicating they are properly seated.
- Attach Storage Devices: Install both HDDs and SSDs by securing them in the designated areas within the case. Connect the SATA cables to the motherboard.
- Install the Graphics Card: If applicable, insert the graphics card into the PCIe slot on the motherboard and secure it with screws.
- Connect Power Cables: Carefully connect all necessary power cables from the PSU to the motherboard, CPU, and any other components.
- Manage Cables: Use cable ties to bundle and secure cables away from fans and airflow routes for better cooling efficiency.
- Final Check: Ensure all connections are secure, screws are tightened, and there are no loose cables. Reattach the side panels of the case.
- Power On: Plug in the power cable, turn on the PSU, and press the power button to start your new PC. Monitor for any issues.
Cable Management and Cooling Solutions
Effective cable management and cooling are critical for maintaining optimal performance and aesthetics. Proper organization of cables not only enhances airflow but also makes future upgrades easier.
- Use Cable Management Features: Most PC cases come with built-in cable management options such as routing holes, tie-down points, and removable panels.
- Plan Your Cable Layout: Before you start connecting cables, plan how you will route them. Aim for a clean look by hiding cables behind the motherboard tray when possible.
- Utilize Fan Placement: Position case fans for effective airflow, typically by following a front-to-back and bottom-to-top airflow direction.
- Invest in Additional Fans: Depending on your components, consider adding extra case fans for improved cooling. Balanced airflow helps maintain optimal temperatures.
- Monitor Temperatures: After assembly, keep an eye on your system’s temperatures using monitoring software. Adjust fan speeds as necessary for optimal performance.
Troubleshooting Common PC Building Issues

Building your own PC can be a rewarding experience, but it’s not without its challenges. From hardware conflicts to boot issues, various problems can arise during and after assembly. Understanding these common problems and their solutions can help you enjoy a smoother building process and ensure your system runs optimally.
Identifying and troubleshooting problems is crucial after assembling your PC. Here are some of the prevalent issues you might encounter, along with their solutions.
Common Problems and Solutions
Sometimes, despite following all the steps, you may face issues that prevent your PC from working properly. Here’s a list of common problems with corresponding solutions:
- No Power: If your PC won’t power on at all, check the power supply connections, ensuring the 24-pin and 4/8-pin connectors are securely attached to the motherboard. Verify that the PSU switch is turned on and that the wall outlet is functional.
- POST Failure: If your system powers on but fails to complete the Power-On Self-Test (POST), it could indicate a hardware issue. Reseat RAM and GPU components, and ensure that there are no loose connections. Check for beep codes or indicator lights on the motherboard.
- Overheating: High temperatures can lead to thermal throttling or shutdown. Ensure that CPU and GPU coolers are correctly installed and that thermal paste is applied properly. Monitor fan speeds and airflow within the case.
- No Display: If there’s no output on the monitor, verify that the monitor is powered on and connected. Try using a different cable or port, and ensure the GPU is seated correctly. If using integrated graphics, remove the GPU and connect the monitor to the motherboard.
Diagnosing Hardware Issues Post-Assembly
After assembly, diagnosing hardware issues can be tricky. Here are some practical tips to help you pinpoint the source of a problem:
- Check cables and connections: Ensure all power and data cables are securely connected. Loose cables can often lead to malfunctions.
- Listen for beeps: If your motherboard has a speaker, listen for beep codes during POST, which can indicate specific issues based on the pattern.
- Use a multimeter: For power supply testing, utilize a multimeter to check voltage outputs against the specifications. An inconsistent power supply can lead to system instability.
- Swap components: If possible, substitute suspected faulty components with known working ones to isolate the issue.
Importance of BIOS Setup and Troubleshooting Boot Problems
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is critical for initializing hardware during the boot process. Properly configuring the BIOS can resolve many boot-related problems.
After assembling your PC, enter the BIOS setup to ensure that all components are recognized correctly. Here are key points to address in the BIOS:
- Check boot order: Ensure that your primary boot device (usually your SSD or HDD) is set to boot first. This can prevent boot issues if your system is trying to boot from the wrong device.
- Enable XMP profiles: For optimal memory performance, enable the XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) settings to ensure RAM runs at its rated speeds.
- Update BIOS: If you’re facing compatibility issues with newer hardware, check the manufacturer’s website for BIOS updates that may improve hardware support.
- Reset to defaults: If problems persist, you can reset BIOS settings to their default state, which may resolve configuration-related issues.
In summary, troubleshooting common PC building issues involves understanding potential problems, diagnosing hardware effectively, and utilizing BIOS settings to ensure optimal system performance. By following these guidelines, you can tackle most challenges that arise during your PC building journey.
If you’re looking for a fun and engaging way to spend your free time, you should definitely check out games poki. This platform offers a wide variety of games that cater to all tastes, whether you prefer action, puzzles, or adventure. With simple controls and vibrant graphics, it’s an excellent choice for anyone looking to unwind and enjoy some quality gaming time.
If you’re looking for a fun way to spend your free time, you should check out games poki. This platform offers a wide variety of engaging games that cater to all interests. Whether you’re into puzzles, action, or strategy, there’s something for everyone. It’s a perfect spot to unwind and enjoy some quality gaming without any hassle.

